What is Enum in java?
- An enum is a class that represents a group of constants. Constants are the final variables and we can not change their values.
- By using the enum keyword we can create the enums in java. Which contains comma-separated constants.
- The naming convention for constants is the upper case only.
Why enums are required in java?
- When we have defined sets of constants like months, days where all possible values are known at compile-time only it’s required to have that set of values in one place and added in enum.
- Enum helps the programmer not to make any mistakes while entering something.
- Enum also helps to improve the readability of the program.
How to create and use enum in java?
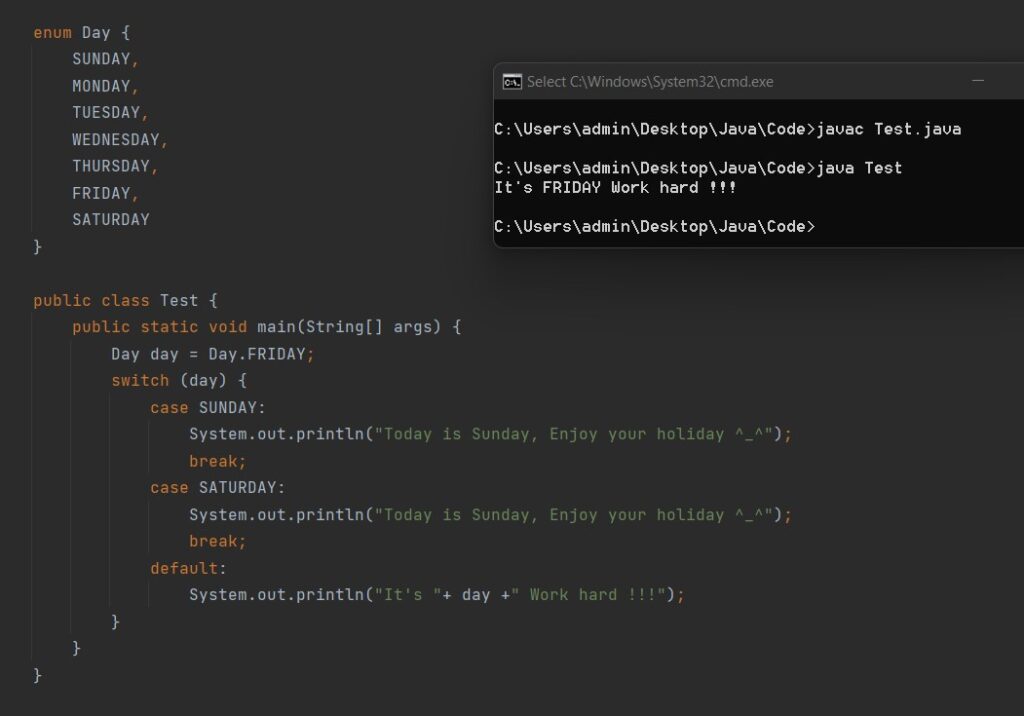
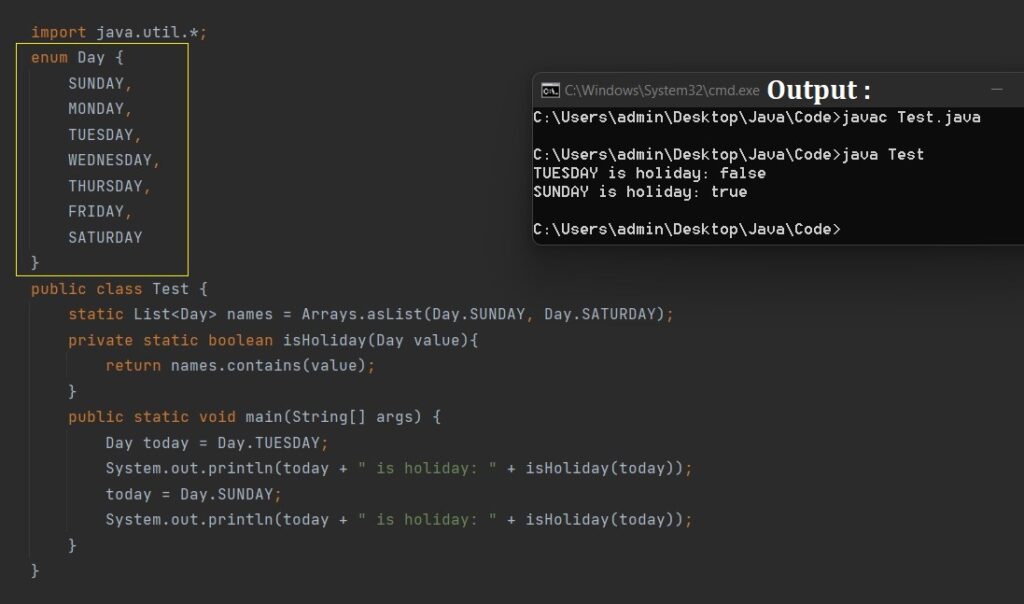
- As shown in the below example we have enum for days. And we are checking if the day is a holiday or not.
- To access the enum values we can directly call by name of the enum followed by the value. Like Day.MONDAY etc.
- Enums can also be used in switch statements.
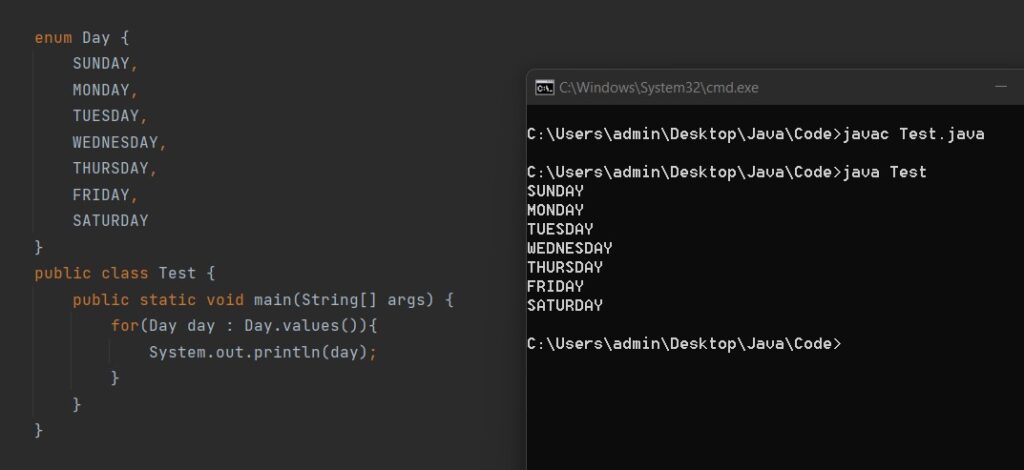
- If we want to iterate over each value of the enum then enum has the values() method which will return all the values inside that enum.
- We can print all the values one by one as shown in the following example.
Notes of enums:
- We can not extend any class in the enum. Since it implicitly extends java.lang.Enum.
- We can implement an interface.
- Enums constructors are always private and final.
- Since constructors are private we can not create an object of the enum using a new operator.
- Constants in enums are by default static and final.
Example for Enum using switch: