G20: A Global Forum for Cooperation

The Group of Twenty, commonly known as the G20, is an international forum consisting of 19 individual countries and the European Union (EU). It serves as a platform for high-level discussions and cooperation among the world’s major economies. Here’s a detailed overview of the G20:
What is the G20?

The G20 is an international forum comprised of 19 individual countries and the European Union. These member nations come together to discuss and coordinate policies related to global financial stability, economic growth, and sustainable development. The G20 member countries represent approximately 85% of the global GDP, two-thirds of the world’s population, and 75% of international trade.
A Brief History
The G20 emerged in 1999, in response to the financial crises of the late 1990s. Initially, it was primarily focused on finance ministers and central bank governors meeting to address global financial stability. However, as the challenges facing the world evolved, so did the G20’s scope and importance. In 2008, at the height of the global financial crisis, the G-20 leaders’ summit was convened for the first time. Since then, it has become the premier forum for international economic cooperation.
Member Countries

The Group of Twenty (G20) comprises 19 countries (Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Türkiye, United Kingdom and United States) and the European Union. The G20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade, and about two-thirds of the world population
Objectives of the G20
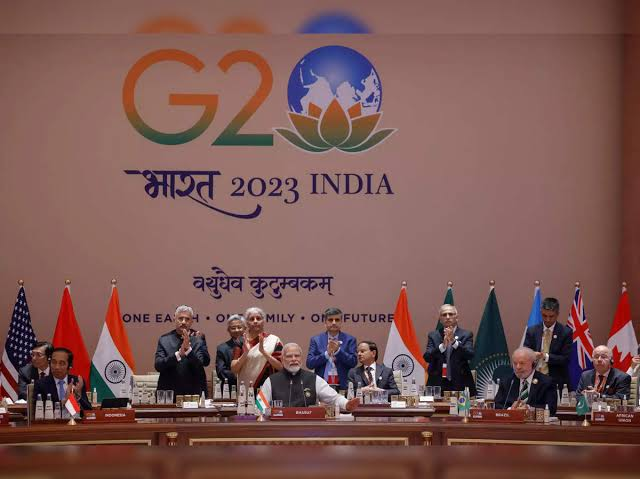

The G20 has several core objectives:
- Economic Stability: One of its primary goals is to ensure global economic stability by promoting policies that mitigate financial crises and promote sustainable economic growth.
- International Financial Regulation: The G20 discusses and coordinates financial regulations to prevent another global financial meltdown.
- Poverty Alleviation: It focuses on reducing poverty and promoting inclusive growth through initiatives like the Action Plan on the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
- Trade and Investment: The G-20 promotes open and fair trade practices and facilitates discussions on international trade issues.
- Climate Change: Climate change and sustainability have become increasingly important topics within the G-20, with discussions on reducing emissions and adapting to environmental challenges.
- Global Health: Tackle global health crises and pandemics, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic.
How G20 Works?
- The G20 Presidency steers the G20 agenda for one year and hosts the Summit. The G20 consists of two parallel tracks: the Finance Track and the Sherpa Track. Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors lead the Finance Track while Sherpas lead the Sherpa Track after Finance Track.
- The G20 process from the Sherpa side is coordinated by the Sherpas of member countries, who are personal emissaries of the Leaders. Finance Track is led by Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors of the member countries. Within the two tracks, there are thematically oriented working groups in which representatives from the relevant ministries of the members as well as from invited/guest countries and various international organisations participate.
The Finance Track is mainly led by the Ministry of Finance. These working groups meet regularly throughout the term of each Presidency. The Sherpas oversee negotiations over the course of the year, discussing agenda items for the Summit and coordinating the substantive work of the G20. - In addition, there are Engagement Groups which bring together civil societies, parliamentarians, think tanks, women, youth, labour, businesses and researchers of the G20 countries.
- The Group does not have a permanent secretariat. The Presidency is supported by the Troika – previous, current and incoming Presidency. During India’s Presidency, the troika will comprise Indonesia, India and Brazil, respectively.
Meetings and Summits
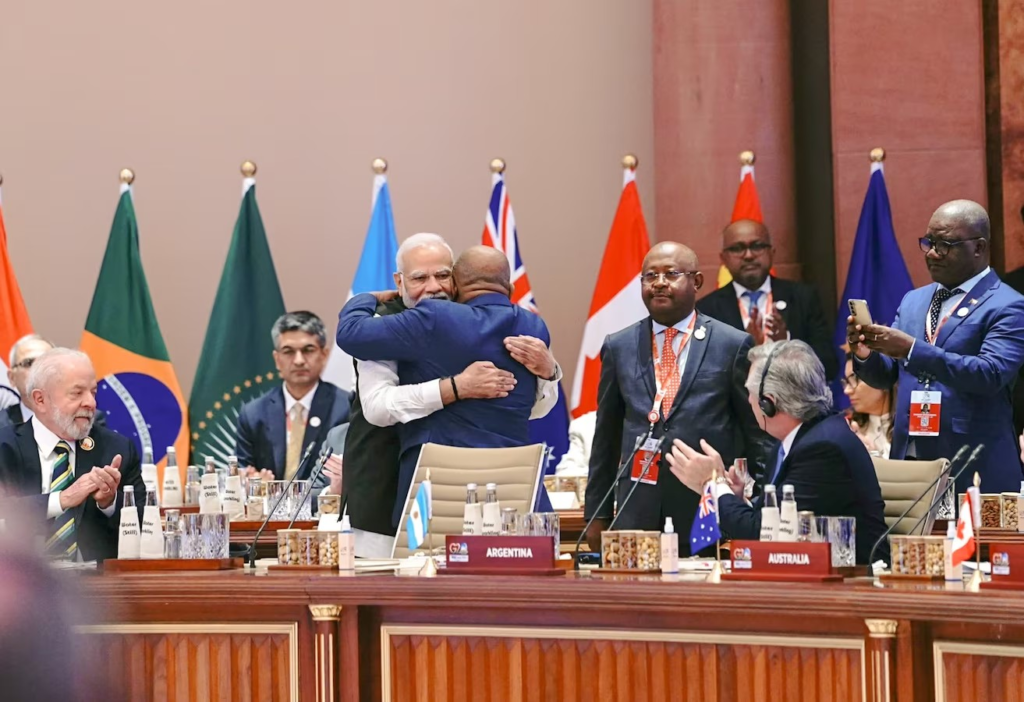

- G20 leaders and officials meet annually to discuss and coordinate policies. The leaders’ summit is the most prominent gathering, where heads of state or government come together to make key decisions.
- Additionally, finance ministers, central bank governors, and other ministers meet throughout the year to address specific issues.
Impact of the G20
The G20 has had a significant impact on the global stage:
- Financial Stability: Its coordinated efforts during the 2008 financial crisis helped stabilize global markets and prevent a deeper recession.
- Trade: It has played a role in mitigating trade tensions and promoting free and fair trade practices.
- Sustainable Development: Through initiatives like the 2030 Agenda, the G20 contributes to global efforts to address poverty, inequality, and environmental challenges.
- Global Health: The G20 has been a platform for addressing health crises, such as the response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
In a world interconnected by trade, finance, and global challenges, the G20 plays a vital role in fostering international cooperation and stability. Its ability to bring together major economies to address pressing issues has solidified its position as a key player in shaping the global economic landscape.
As the world continues to face complex challenges, the G20 will remain a forum where nations can come together, share ideas, and work towards a more stable, equitable, and sustainable future.
Write with us✍?
TeamUgtWorld warmly welcomes everyone! If you have something on your mind that you’d like to write about, we invite you to publish your content on our platform @Ugtworld. To learn more, please click on the link provided below.


